Technologies for every step of water treatment Wastewater Treatment Plants
Back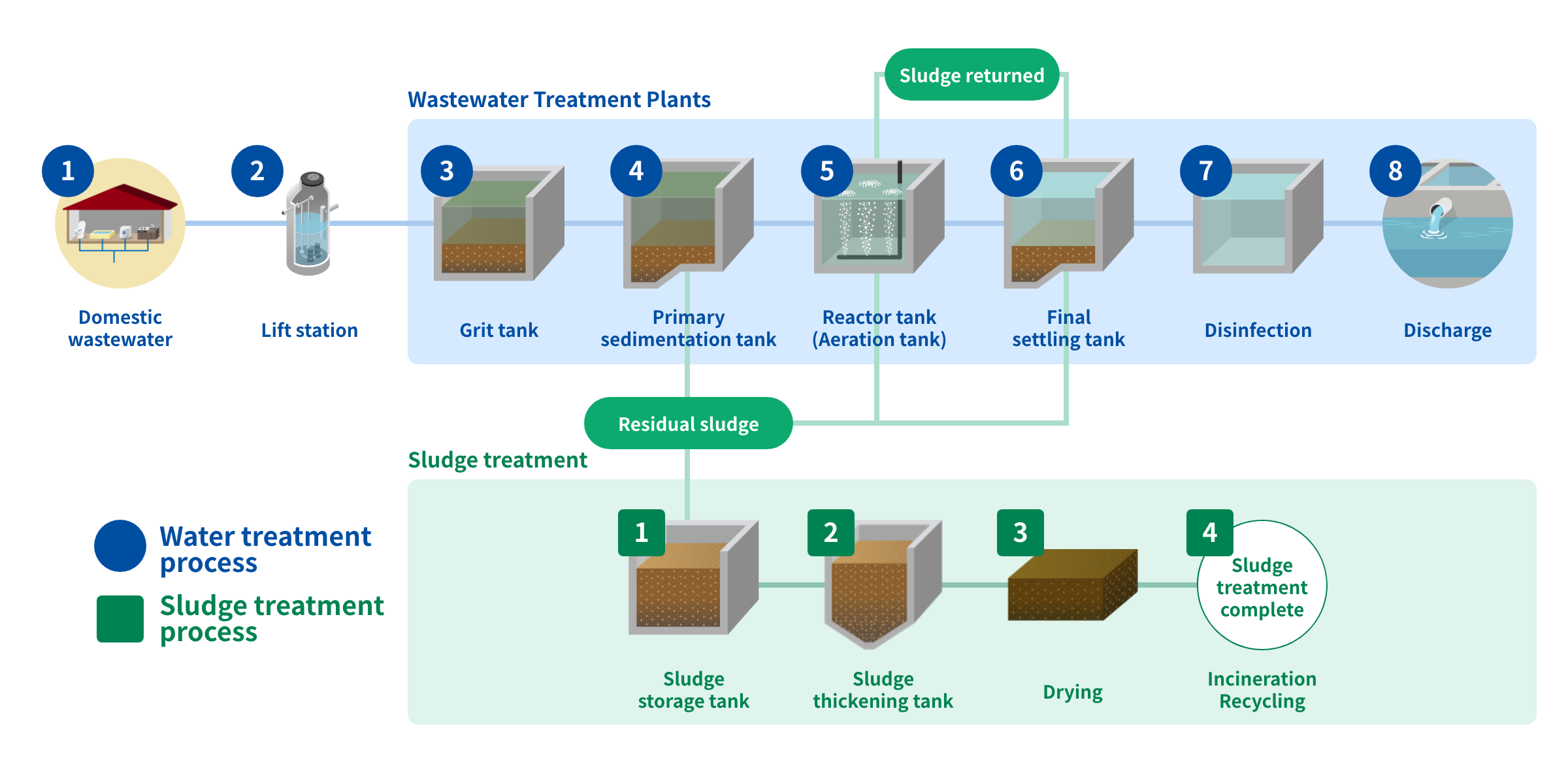
1Domestic wastewater

Household wastewater
Water used in everyday living, such as drainage from the bath, kitchen, and toilet, is emitted as wastewater.
2Lift station

Wastewater collection
Wastewater from nearby homes flows to a lift station and from there is pumped to a wastewater treatment plant.
treatment plant
3Grit tank / Pump

The first process of wastewater treatment
In the grit tank, wastewater first passes through screens to remove coarse sand and large debris.
4Primary sedimentation tank

Fine silt and contaminant removal
Wastewater flows through slowly, allowing solids (raw sludge) to settle to the bottom for removal.
5Reactor tank (Aeration tank)
Purification by bacteria
Bacteria in the water feed on contaminants, cleaning the water.
Air is mixed into the water so that bacteria have enough oxygen to do their work.
-
 Submersible Mixer
Submersible Mixer
SM/SME -
 Submersible
Submersible
Aerator -
 Vertical
Vertical
low-power
mixer SVM -
 Roots blower
Roots blower
ARH -
 Turbo blower
Turbo blower
STX series
returned
Why return the sludge to the earlier stage?
The number of bacteria in the reactor (aeration) tank gradually decreases, reducing treatment efficiency.
The sludge at this stage primarily consists of bacteria.
Returning this sludge to the reactor tank boosts the number of bacteria there, stabilizing treatment performance.
6Final settling tank
Just the clean water is taken out
Bacteria that have eaten contaminants slowly settle out, forming activated sludge; some of this sludge is returned to the reactor tank.
7Disinfection
Final process of wastewater treatment
With the disinfection of the water taken out, its treatment is complete.
8Discharge

Part of a clean water cycle
The treated, clean water is discharged into streams or the ocean.
Eventually, it will form clouds and fall back to land as rain.
1Sludge storage tank

Homogenizes sludge thickness and prevents putrefaction
To prevent sludge from putrefying, it must be agitated and supplied with adequate oxygen.
What is residual sludge?
Residual sludge is formed by bacteria that settle out of the water after eating contaminants, which makes them heavier.
2Sludge thickening tank

Easier sludge storage
The residual sludge in the sludge storage tank is mechanically concentrated and dehydrated using specialized equipment.
Why thicken the sludge?
The residual sludge has a high water content. Removing this water with dehydrators reduces the weight of the sludge, in turn reducing the cost of its disposal as industrial waste.
3Drying
Reducing waste disposal costs and recycling
Drying the concentrated sludge further reduces its weight, cutting industrial waste disposal costs.
Depending on the treatment methods used, the sludge may be recyclable.
Please contact our sales department for further details.
Inquiry form



