Environmental Protection Activities
The Group continuously monitors CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and other factors as it works to facilitate the reduction of its environmental burden.
Measures to reduce the environmental burden and combat climate change
Since the 1980s, we have been working for many years to prevent
global warming by making effective use of fossil fuels (natural
resources) mainly at our plants.
In 2012, the Company was designated as a specified business
operator under the revised Act on Rationalizing Energy Use, and
we have been engaged in Company-wide efforts to further
conserve energy.
In addition, from FY2022, we have set a new goal of
reducing total CO2 emissions by 38%*1 by FY2030,
and we are implementing measures aimed at
achieving this goal.
- *1 Compared to our peak value recorded in FY2017.
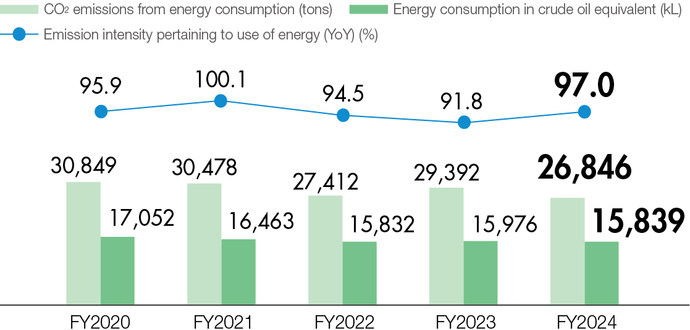
Activities in FY2024
In FY2024, we installed solar power generation panels on the roof
of new “large-scale submersible pump operation inspection
equipment” that we constructed at the Ono Plant, a production
base for fluid products. Electric power obtained through the panels
was utilized to contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions (52
t-CO2/year). We have also worked to develop a company-wide
system concerning the introduction of solar power generation
equipment and procurement of CO2-free electric power as
environmental investments.
In addition, we have put a system in place to manage the
CO2 emissions of major Group companies in Japan and overseas
and measure Scopes 1 and 2 emissions on a consolidated basis.
Waste reduction
The Company is committed to reducing waste and recycling through the 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) as well as Refuse (not accepting things that will end up as garbage). In our efforts to realize a recycling-based society, we have also set new targets in FY2022 of reducing total waste emissions by 10% *2 by FY2030 and achieving a recycling rate*3 of 99% or more.
- *2 Compared to FY2020
- *3Recycling rate: Amount of waste recycled/ Total amount of waste generated × 100 (%)
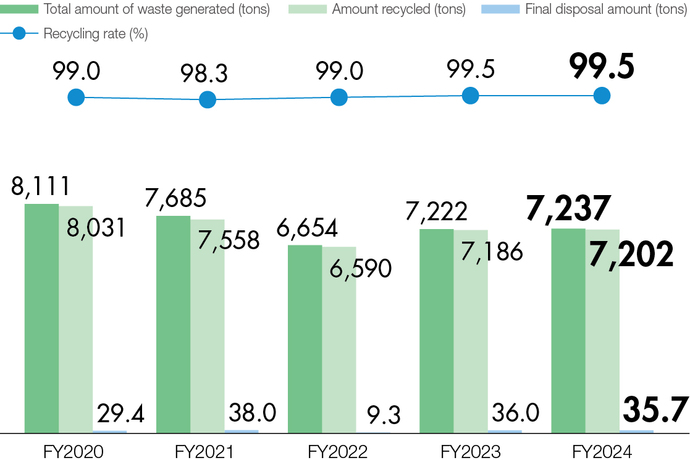
Activities in FY2024
We have been engaged in efforts to minimize the amounts of input materials and waste in line with a further improved yield in manufacturing and facilitate the conversion of waste to resources with value by thorough separation and sorting.
プラスチック廃棄物排出量の削減
当社は、事業活動に伴って発生するプラスチック廃棄物の排出量について、売上高原単位で2021年度比9.0%の定常的な削減(2030年度)を目標に掲げ、削減に向けた取り組みを進めています。
2024年度の売上高原単位は、2023年度に比べて増加したものの、依然として低い水準にあります。この低水準には、事業構成の変化といった一時的要因が影響しています。また、これらの要因が順次解消された場合には、売上高原単位は増加に転じると推定されます。
こうした状況を踏まえ、当社は工程の効率化、分別廃棄の徹底、再資源化の推進など、環境負荷低減に向けた取り組みを一層強化し、目標の達成を目指してまいります。
| 2021年度実績 | FY2022 results | FY2023 results | 2024年度実績 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 排出量(t) | 545 | 509 | 540 | 577 |
| 売上高原単位(kg/百万円) | 4.19 | 4.00 | 3.55 | 3.61 |
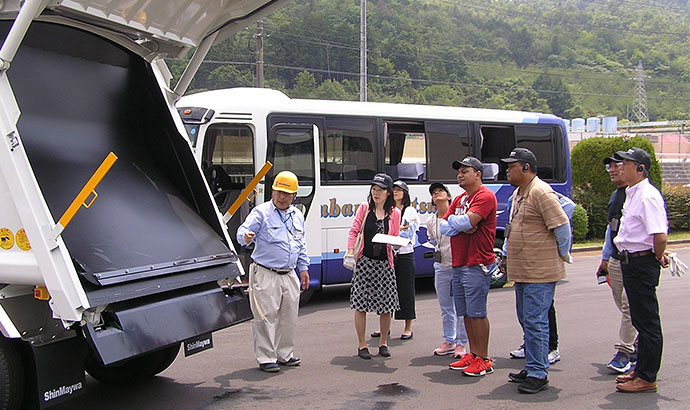
Cooperating with JICA Knowledge Co-Creation Program “Basics of Solid Waste Management”
In accordance with its Sustainability Management Policy, the Group aims to
contribute to society at large through its business activities. Since FY2011, we
have been cooperating with the Knowledge Co-Creation Program “Basics of
Solid Waste Management,” a training program hosted by the Kansai Center of the
Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
This training program was organized by the Learning and Ecological
Activities Foundation for Children (LEAF), a non-profit organization commissioned
by JICA, for government and municipal officials in the Pacific, Asia, Latin America
and other regions. The objective of the program is to learn about solid waste
management in partnership with private sector and civil society. The curriculum
consists of lectures and on-site tours on such topics as waste treatment in local
governments in Japan, building a recycling-based society, and recycling of
recyclable materials. We took the group to the Hiroshima Plant, and following a
lecture titled “Our Initiatives as a Refuse Compactor Manufacturer” in the morning,
we gave a tour of the production site on the theme of “Training on the Operation
and Repair of Refuse Compactors” in the afternoon to provide the group with
explanations on operation methods and safe handling using actual vehicles. This
training was resumed from FY2023 as it had been suspended from FY2020 to
FY2022 due to the COVID-19, and was attended by participants from the
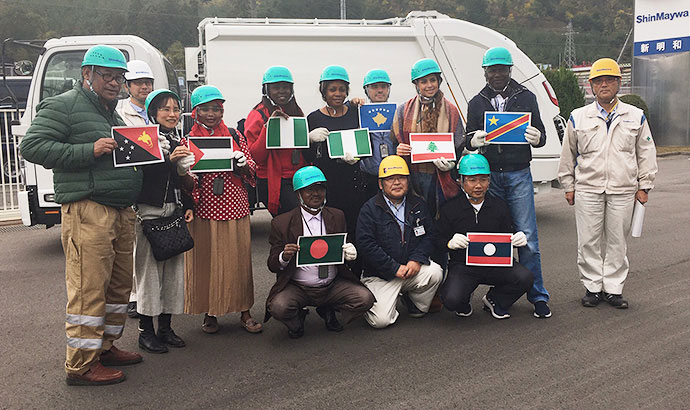
countries shown below in FY2024.
By continuing to actively cooperate with JICA trainings, we aim to
contribute to solving the world’s waste issues with our refuse compactors.
| Date | Country | Number of trainees |
|---|---|---|
| September 3, 2024 | Cambodia, Ethiopia, Lebanon, Philippines, South Sudan, Sudan, Vanuatu | 7 |
| December 5, 2024 | Bhutan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Kosovo, Republic of Macedonia, Papua New Guinea, Serbia, Republic of Turkey, Uzbekistan | 9 |


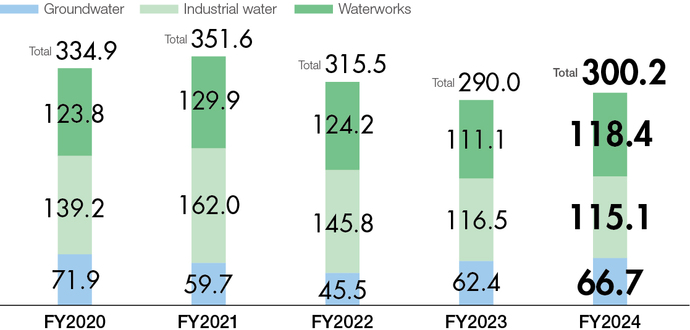
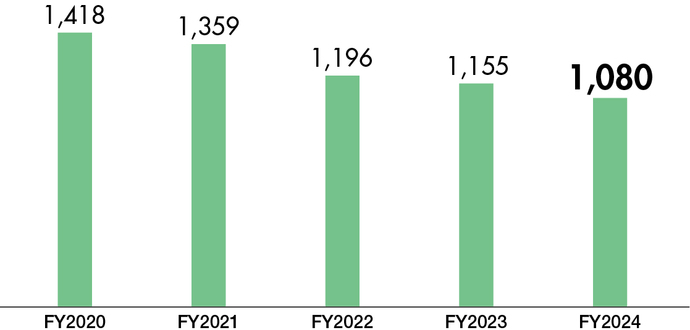
Protecting Water Resources and Reducing Water Use
Saving water, a limited and precious resource, also leads to energy
savings in the water purification process. Our plants are thus committed
to proper management of both its water consumption and wastewater
discharge, and in FY2024, as in the previous years, there was no noncompliance
with laws or ordinances.
Although the Company evaluates that its water risk is low owing to
its limited water consumption, the Company will take climate change and
the local water situation into account and enhance efficiency in the
sustainable use of water resources. The Company will continue monitoring
its water consumption and promote water management that emphasizes
coordination with local communities.
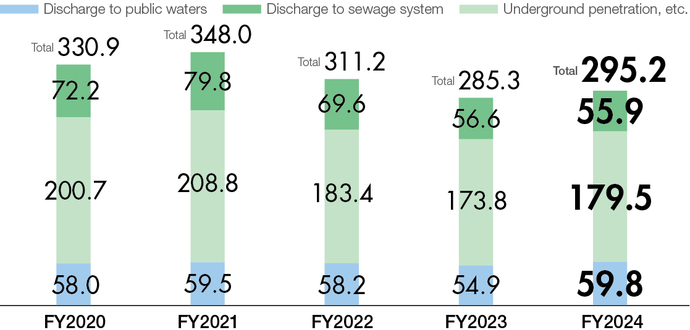
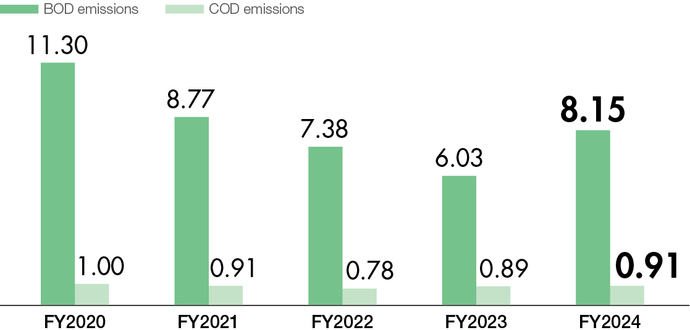
Reducing emissions of pollutants
For substances discharged from our plants into the atmosphere and water, we set voluntary emission limits that are stricter than legal regulations*4 in our efforts to reduce our environmental impact.
- *4(Examples) NOx: Approximately 30–70% of the legal limit; BOD: 50% of the legal limit (Aircraft Division Konan Plant).
Management of chemicals
We continually work on the proper management of chemicals, and in FY2024, as in the previous years, non-compliance with or a violation of laws or ordinances was not confirmed.
The Company’s fluorocarbon emissions were 17.3 t-CO2 in FY2024. We stably mange emissions through the appropriate maintenance and management of refrigerant equipment.
Regarding substances subject to PRTR system, the release and transfer volumes were 116,300 kg and 12,863 kg, respectively, and both volumes were properly managed.
The Company will continue to thoroughly comply with laws and ordinances and strive to further reduce its environmental burden through introducing alternative substances and reviewing manufacturing processes.
